COVID-19 cure to be developed within this year
COVID-19 cure to be developed within this year
Posted July. 22, 2020 07:49,
Updated July. 22, 2020 07:49
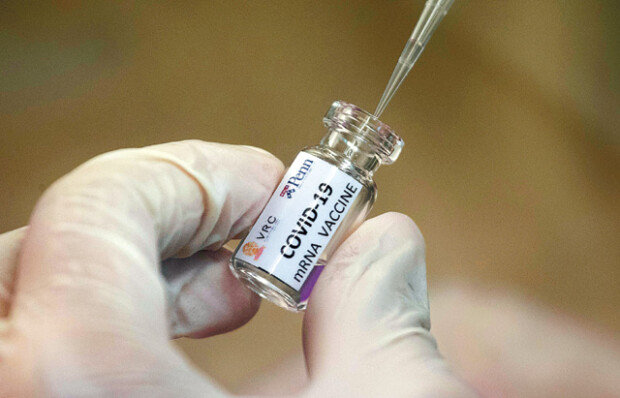
COVID-19 treatments could be developed by the end of this year, unlike vaccines which are expected to be commercially available next year.
There are four main ways of developing cures for infectious diseases: drug repurposing, plasma, antibodies and new drugs. Drug repurposing refers to a process to develop a treatment using existing medicine. For plasma treatment, antibodies of patients who have recovered from the disease are collected from their plasma, while antibody treatment development involves tweaking genes to produce antibodies. As developing a new drug takes a long time, pharmaceutical companies are focusing on the first three methods.
In South Korea, GC Pharma, Bukwang Pharmaceutical Company and Celltrion have already begun trials of COVID-19 treatments. Bukwang Pharmaceutical Company is conducting a Phase 2 trial for its repurposed medicine at Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University Ansan Hospital and six other hospitals.
GC Pharma has completed its Phase 1 trial for its plasma treatment and is planning to submit application for a Phase 2 trial to the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety by the end of this month. “Production of the plasma medicine begun on Saturday and will be ready for clinical trials by the end of August,” said Kwon Jun-uk of the central epidemic prevention team.
According to Korea National Enterprise for Clinical Trials, 11 trials were approved for COVID-19 treatments as of July 10.
Mee-Jee Lee image@donga.com



![연금 개시 가능해지면 年 1만 원은 꼭 인출하세요[은퇴 레시피]](https://dimg.donga.com/c/138/175/90/1/wps/NEWS/IMAGE/2026/02/20/133390850.4.jpg)
![취권하는 중국 로봇, ‘쇼’인 줄 알았더니 ‘데이터 스펀지’였다?[딥다이브]](https://dimg.donga.com/c/138/175/90/1/wps/NEWS/IMAGE/2026/02/20/133391101.1.png)

