Korea is not safe zone from mosquitoes
Korea is not safe zone from mosquitoes
Posted February. 20, 2016 07:32,
Updated February. 20, 2016 08:05
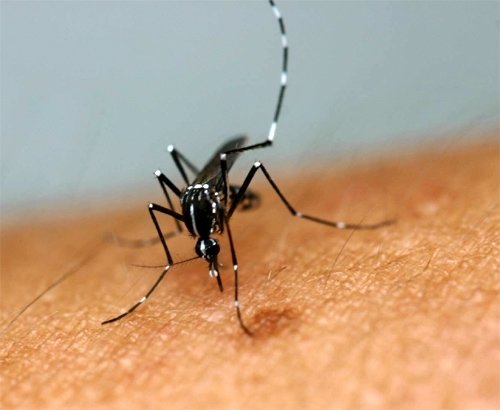
Health authorities are particularly paying attention to "dengue fever," which is an epidemic in tropical and subtropical regions such as Southeast Asia, India and Africa.
Dengue fever is carried by infected yellow fever mosquitoes and Asian tiger mosquitoes. The latter one was confirmed to inhabit in Korea in 2009. The inhabitation density of Asian tiger mosquitoes is not so high yet. However, more mosquitoes will be active if the average temperature rises in Summer and continuous localized torrential downpour makes a humid atmosphere.
Dengue fever accompanies symptoms such as headache, fever and muscle pain. The disease is so contagious that the number of the infected around the world is amounting to 50 million to 100 million. The fatality is four percent (20,000 out of 500,000) among serious patients. However, the World Health Organization (WHO) and other organizations categorize the disease as one of the most dangerous contagious diseases because of its high infection rate.
"Dengue fever is usually carried by people who return to Korea after travelling abroad. It is very difficult to inspect all people who return from overseas with limited personnel," said an official of the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on Friday. Forty-one percent (164) of people who were infected by a contagious disease in 2014 was dengue patients, while the number increased to 259 last year.
"Chikungunya fever," which is similar to dengue fever but causes severe pain to joints, is also carried by Asian tiger mosquitoes. Since the first Korean was found to have been infected by Chikungunya fever in 2013, an average of one person has been infected by this disease.
Also is rising the risk of Japanese encephalitis and malaria, which are mosquito-borne diseases and are already naturalized in Korea. This is due to the global warming that will bring hot weather as soon as in April, bringing forward mosquito season.
The number of malaria patients was 638 in 2014, about an increase of nearly 100 year-on-year. In addition to this, the number of malaria patients who were infected overseas and returned to Korea increased by 33 percent.
임현석기자 lhs@donga.com





![연금 개시 가능해지면 年 1만 원은 꼭 인출하세요[은퇴 레시피]](https://dimg.donga.com/c/138/175/90/1/wps/NEWS/IMAGE/2026/02/20/133390850.4.jpg)
